Open-source intelligence (OSINT) collects and analyzes information from publicly available sources to obtain valuable and reliable information. The scope of OSINT is not limited to cybersecurity as it includes corporate, business, military intelligence, and many other information-based areas.
This article is suitable for anyone who wants to learn something useful, whether they are recruiters, marketing managers, cybersecurity engineers, or just people interested in how OSINT works. We will explain how to conduct OSINT people searches properly, collect information for competitive intelligence or find vulnerabilities in your organization.
There are many OSINT tools, and it makes no sense to describe each of them. So, we will introduce you to the best of them, and you'll learn about the general OSINT approach and specific methods for different needs. If you don't know where to start, read the article.
OSINT steps
- Start your search based on the information you already have. For example, email, name, address, phone number, etc.
- Figure out what you want to find or get.
- Collect data.
- Analyze what you have found.
- Summarize collected data.
- Analyze the assumptions and double-check they are correct.
- Write a report.
Real name search pattern
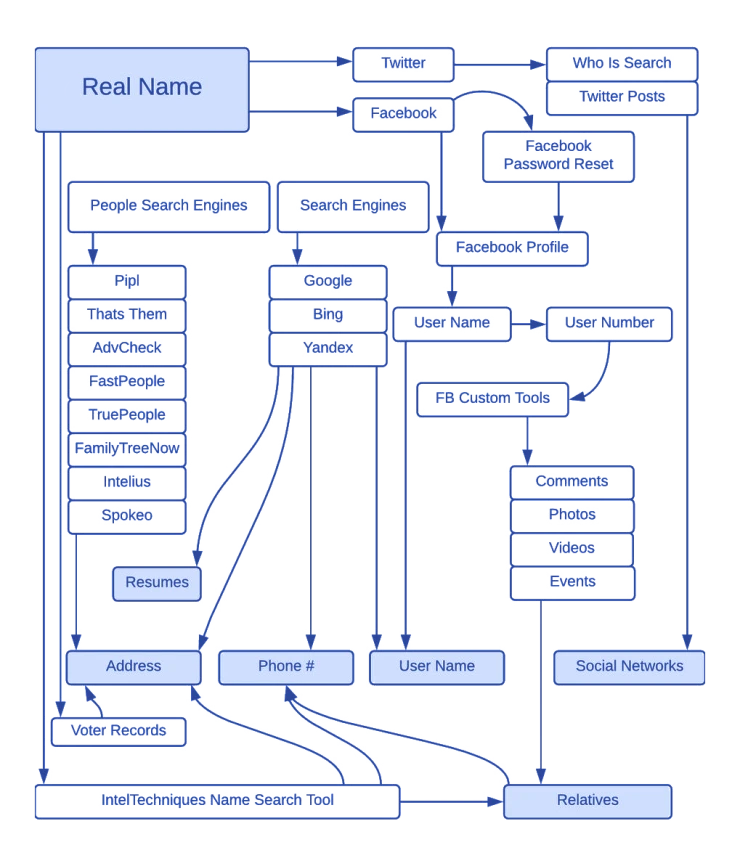
Governmental resources
You can find information about people and organizations on the Internet, and its accessibility depends on the country. We will deliberately not expand on this as the government resources might not be relevant to the general public. Basically, you just need to know that such resources exist, so use regular search queries to find them. It's not difficult at all.
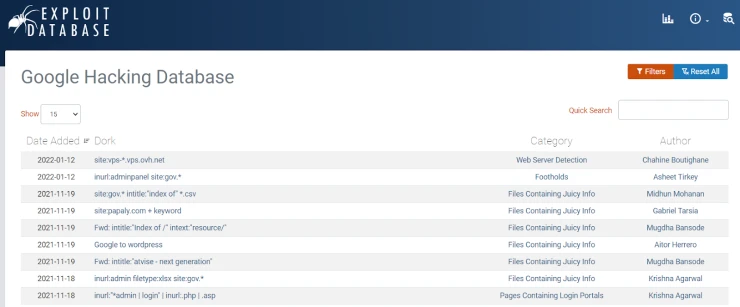
Google Dorks
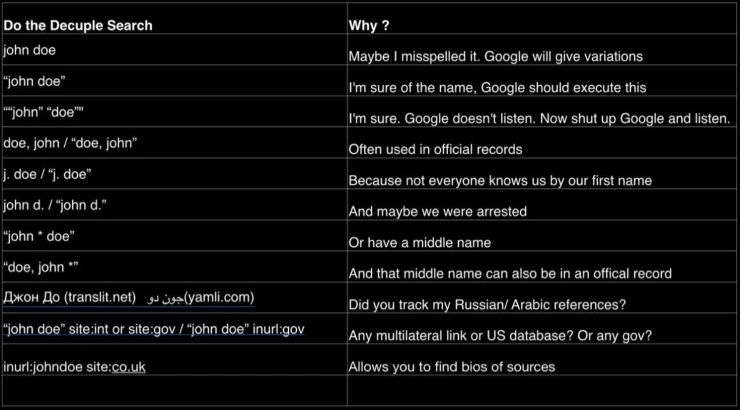
Google Dorks or Google Hacking is a technique used by the media, intelligence agencies, and security professionals. It is necessary to detect hidden information and vulnerabilities that are undetectable on public servers. This method helps to use ordinary website search queries to their fullest extent and find discreet details. For example:
- “john doe” site:instagram.com causes Google Search to do an exact match when searching Instagram.
- “john doe” -“site:instagram.com/johndoe” site:instagram.com hides a person’s posts but shows the comments they have left on other people's posts.
- "john" "doe" -site:instagram.com excludes Instagram from the search and shows the exact match of the first and last name in various variations.
- “CV” OR “Curriculum Vitae” filetype:PDF “john” “doe” finds person’s CV in PDF format
By default, Google will try to form your keyword the way most people search for it. So you should enclose individual words in quotation marks if you are sure of their spelling to search for an exact match of your query. Interestingly, with the right Google Dorks queries, you can see the comments and likes of closed accounts.
Keep in mind that other search engines besides Google can give different results. For example, you can try using advanced search queries in Bing, Yandex, or Yahoo.
Full list of Google Dorks
People search
Some websites specialize in finding people. So, you can find interesting information by entering your real name, username, email address, or phone number.
- https://x-ray.contact/
- https://www.spokeo.com
- https://people.yandex.ru
- https://www.fastpeoplesearch.com
- https://www.familytreenow.com
- https://www.beenverified.com
- https://thatsthem.com
- https://www.truepeoplesearch.com
These sites allow users to remove their information upon request. However, this data will most likely be back in a few months since most databases are constantly duplicated. Certain companies own these databases, and even if a person removes their data from the list, this data can be copied to a new domain.
That is good news for OSINT investigators: if someone deleted their information, it would reappear in a new place soon enough. One way to find people deleting their data over and over again is to go to one of these sites. Next, you need to use a cited unique paragraph search on Google and find all the company's sites. Perhaps, one of them still has information on your target.
User name
To search for a person by username, you need to know it. Often, you can figure out a user's name from a combination of first and last name, email, or website domain. Take the information you already have and use a reverse username search by using the following sites:
- socialcatfish.com
- usersearch.org
- peekyou.com.
Use a handy scheme below to make your search more convenient/
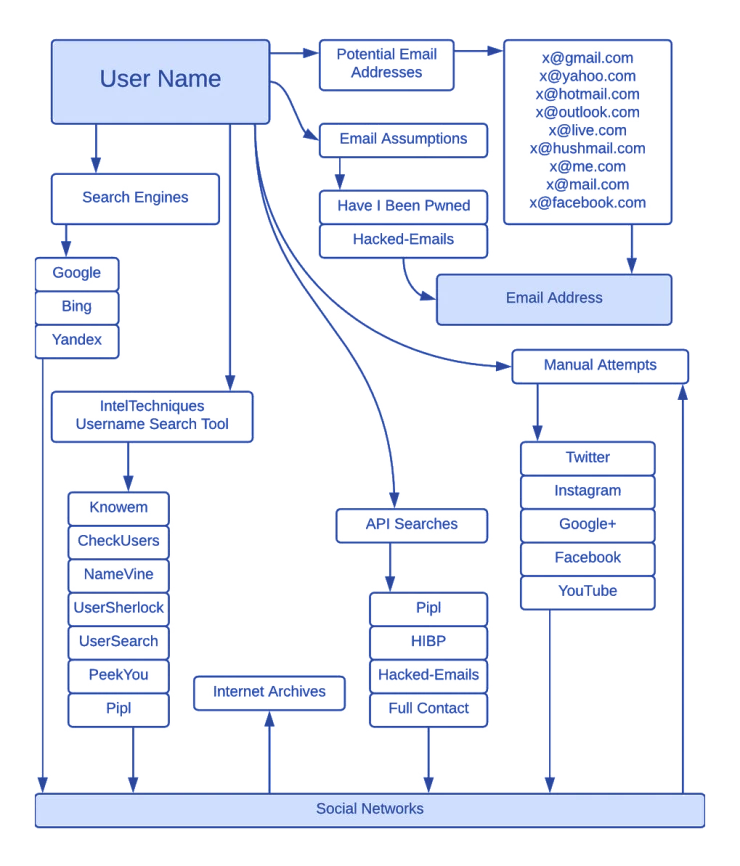
Username search with Google Dorks
Google Dorks can also be used to find the username as URL searches can give good results because URLs usually contain usernames.
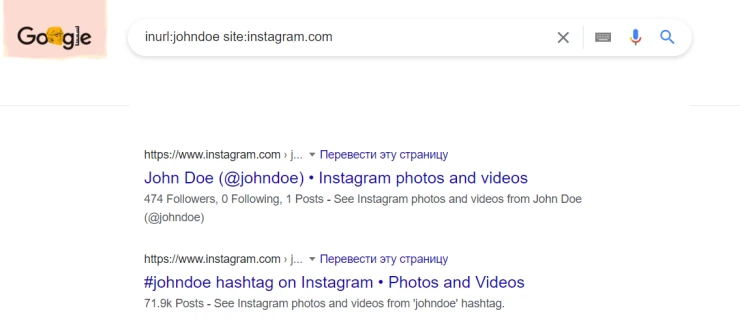
- inurl:johndoe site:instagram.com searches for Instagram links containing "johndoe" in the field.
- allinurl:john doe ny site:instagram.com searches for "john", "doe", and "ny" in Instagram URLs. It's similar to inurl, but unlike inurl, it supports multi-word searches.
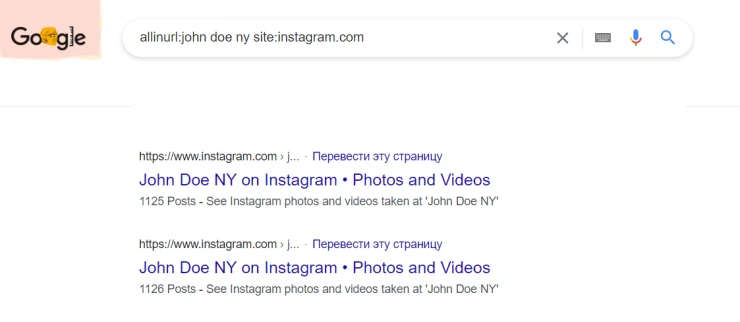
The list of words you get will depend on the success of your search using the previous methods. You can use it when you need to experiment with numerous username variations. To compile such a list of words, you can use a special Python script helping to automate the process.
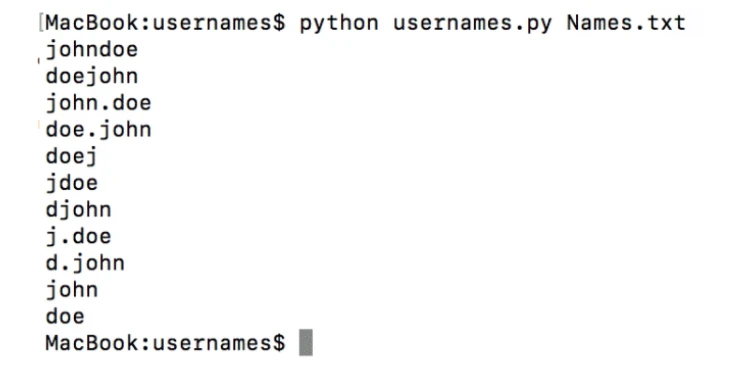
Search by username
Quite a few sites search by username, but our task is to give you those that really work. If we talk about high-quality services to search by username, these two are among the best:
Often the search result for these services is different, so for the best results, we recommend using both.
If the online services don't work, you can use the What's My Name project with more advanced tools like Recon-ng and Spiderfoot.
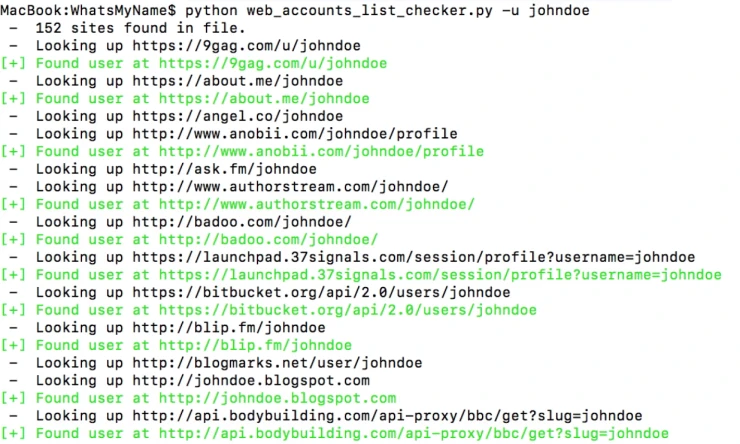
It is important to understand that you will get false positives if someone else is using the same username. It's part of the job; just be prepared for it.

Email addresses
Below is a workflow diagram for finding information about a person based on an email address.
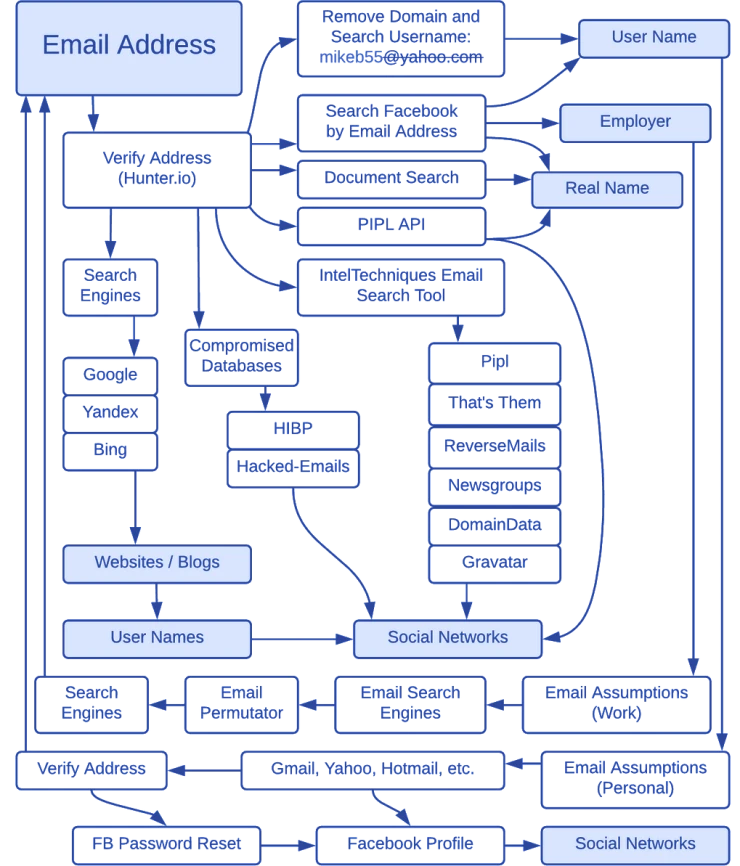
We can also use the tool we already know to search for information or a person using email - Google dorks. Try the following queries:
- “@example.com” site:example.com finds all available email names on the given domain.
- HR “email” site:example.com filetype:csv | filetype:xls | filetype:xlsx finds contact lists of HR employees in a specific domain
- site:example.com intext:@gmail.com filetype:xls gets email IDs for a Google domain.
Email tools
- Hunter is a tool to find email addresses in a specific domain quickly.
- Email-permutator is an to find the email addresses of people you need to contact.
- Proofy is a software to conduct mass verification of email addresses. Extremely useful when you want to check dozens of addresses right after you've created a list with Email-permutator.
- Verifalia is a free email address checker, but you'll have to register if you want to check more addresses.
Compromised databases
Cases of data leakage from popular services happen more often and allow researchers to find more information that should be hidden. If you need a list of services used by your target, use Have i been pwned? site.
You can check if an account has been compromised and see the danger of online attacks on your privacy. You can check your email address and find out if your data is in one of leaked databases.
Another tool for finding compromised email addresses is DeHashed. If you have a free account, it works similar to Have i been pwned? site, but you can see passwords in plaintext or hashes if you've subscribed. In particular, we need this data to find out if it has been used on any other websites. It is also an additional way to see services a person uses or has used.
Phone number search
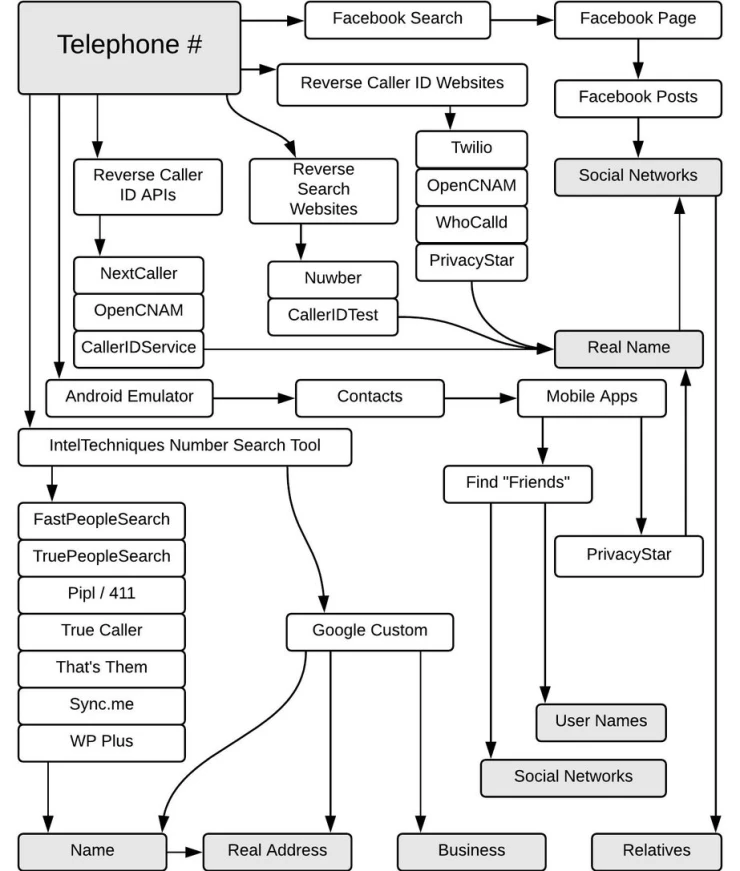
Some people link their social network profiles to their phone numbers and email addresses. That's why sometimes we can find a person by entering their phone number in the Facebook search box.
To find a person's phone number, you can use the who Calledme.com website to search databases of phone numbers provided by users. You can search for subscribers from America and Europe. For mobile devices, you can use the following applications:
Getcontact - https://www.getcontact.com/
EveryCaller.com - https://www.everycaller.com/
PrivacyStar.com - https://privacystar.com/index.html
Many services and companies provide reverse search by phone number. Their capabilities and availability of information depend on the country's legislation, so look for the one that is right for you.
PhoneInfoga
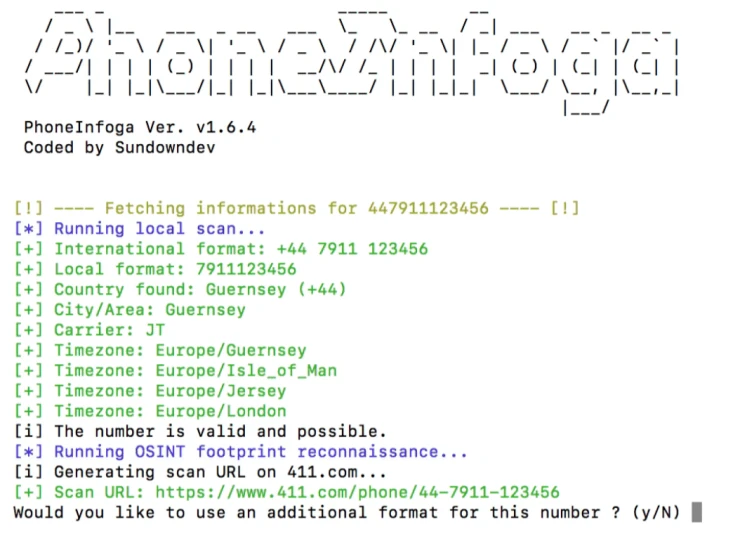
You can scan phone numbers using only free resources with PhoneInfoga. As for international phone numbers, the first step is to collect all the essential information accurately, including country, region, and provider. You can look for traces on search engines to identify the owner through the VoIP provider.
Important: PhoneInfoga actively searches during operation. Google doesn't like it very much and uses Captcha to restrict us. The system displays a message like:
1 (!) You are temporarily blacklisted from Google search. Complete the Captcha and press ENTER.
You will need to enter Captcha in the browser and press enter in the program to continue the search. It shouldn't be a problem if your goal is to check a couple of numbers. But if there are many numbers, solving the Captcha will quickly tire you. The way to solve this problem is to set up an API and activate a custom Google search.
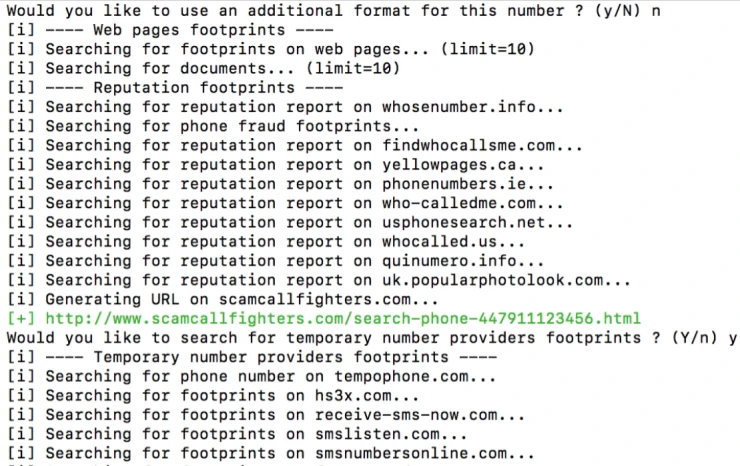
Usually, when looking for information by phone number, we indicate one variant of its writing. It can become a problem because if we search for +1237373627, we will not get other combinations of this number, for example, +(123)-737-3627, in the search results. Therefore, if you want to find different number variants, you need to use the configured Formatting. Study the format used in the country where the number belongs. In France, the number is often indicated in the format 01.02.03.04.04 or 04 03 02 01. The most popular format among Americans is 123-456-1234, while Russia uses +7 (911) 1234-567.
Android Emulator
The emulator can run most Android applications without problems, but some of them may not work as you expect. For example, we found that Viber has issues with VoIP phone numbers. However, the emulator has a number of advantages, including the protection of your real accounts and phone number, as well as the ability to replace GPS coordinates.
Write down the phone number of a person in the contact book and open the contact list of such messengers as Telegram, Viber, WhatsApp, etc. Usually people add their photos, real names, and contact information.
Here are some of emulators:
Bluestacks originally created for those who love to play. However, it allows you to run other applications. Works with all operating systems and does not require a virtual machine.
- Genymotion works on Windows, Mac and Linux and has various virtual devices. A free version for private use is quite popular among developers. Use the guide for setting up and using the emulator.
- AMIDuOS uses Windows system drivers to provide near-native Android performance. It’s easy to install and fast but only compatible with Windows. The cost of the app is $10.
Domain name
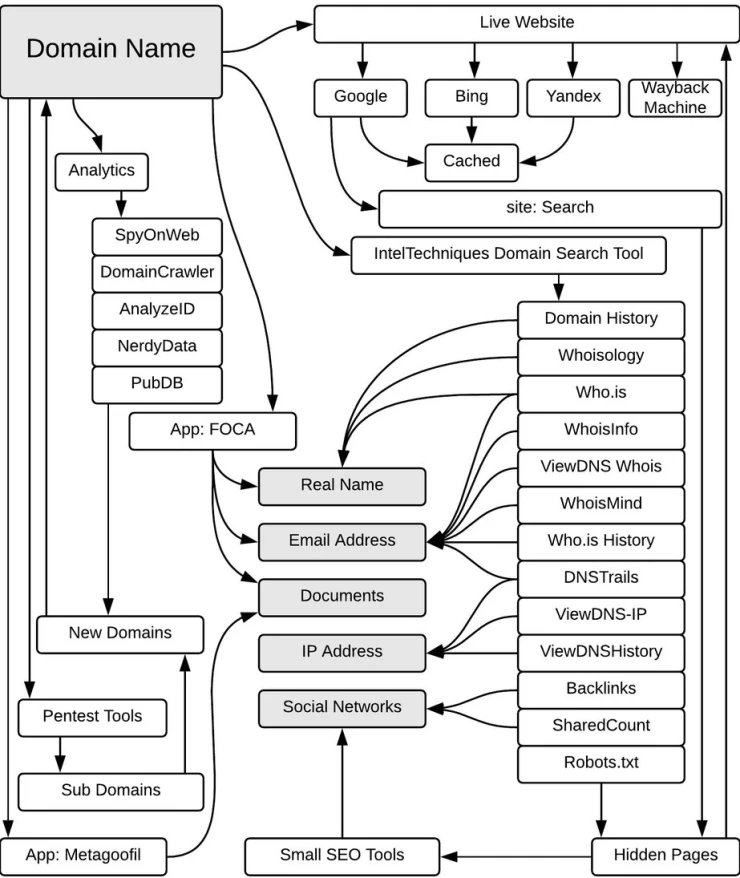
When a person or an organization has a website, you need to know how to get information about it. During the investigation, we can find out what operating system and software version the website uses, or see personal information on its owners. We strongly recommend exploring the environment without directly intervening with your target. This method is called passive reconnaissance as a researcher uses tools and resources to obtain additional information without interacting with the systems. Read how to use this method remaining unnoticed below.
Google Dorks
We have already mentioned Google Dorks several times, but it is worth noting that it fully fits into the concept of a passive method of collecting information. Below are some queries that may be useful when researching a domain:
- site:example.com searches for only a specific website or domain.
- filetype:DOC finds DOC files or other specified types (PDF, XLS, and INI). By the way, you can search for multiple file types in a single query. Separate the extension request with the symbol "|".
- intext:word1 finds the specific word on pages and websites.
- allintext: word1 word2 word3 - searches for all the given words on the page or site.
- related:example.com displays web pages similar to the specified web page on a list.
- site:*.example.com shows all subdomains. You can use an asterisk when searching instead of a whole word or words.
Whois
Whois provides information about users and owners of Internet resources, including domain names, IP blocks, and autonomous systems. Many resources are similar to Whois, but we selected a few of the most useful to you.
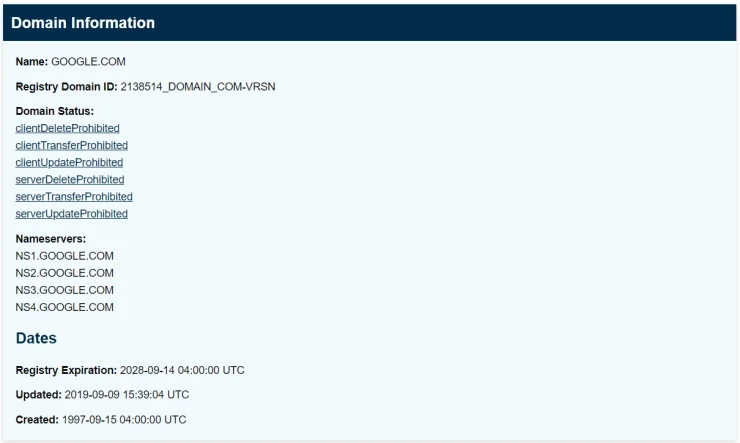
Reverse Whois
Using a reverse search with Whois, you can find domains with the same organization name or email address as the domain you are browsing. For example, if you study the activities of John Doe Inc., you can see all other domain names registered under that name. One handy resource for reverse search is Viewdns.info, which has many features and tools.
Same IP
Sites hosted on the same server as your target website are also interesting to us. For example, you can find subdomains by using AtSameIP and SameIP.org.
Passive DNS
You can see which IP address resolves to which name or which name resolves to which IP address using DNS records. If it’s not enough, you can use passive DNS records. In this way, you can get a helpful permission history based on all the names that were resolved on the IP address. We recommend RiskIQ Community Edition because it provides more information than passive DNS. You can also use VirusTotal or SecurityTrails for these purposes.
Internet archives and cache
The WaybackMachine helps to find archived versions of websites and recover deleted pages.
Archive.today is an analog of the WaybackMachine, where you can add screenshots of URLs manually.
Sometimes search engines cache pages that have been removed but not archived. Look for such pages on CachedView or make a request to Google using the following query: cache:website.com.
Couldn’t get the desired result? Check the cache in other search engines. It is essential to understand that the cache shows when the page was last indexed, which means that the information may not be up to date and the images have been removed.
If you need to track changes on the site, you can do it automatically by using the Visoalping resource. It will send you screenshots if the site has changed.
Reputation, malware, and referrals analysis
To find out whether the site can be trusted, you can use free online tools. If you have any suspicions about the resource you want to visit, you can use free online tools. While the test by itself won't give you accurate results, it can still show you related domains.
SiteWorthRraffic. This service estimates the value of a website: daily revenue, unique daily visitors, and daily page views of any submitted website or domain name. Please note that all estimates are approximate.
Alexa. Initially, Alexa was just a toolbar that showed important information for each visited site; for example, the number of the resource pages, who registered it, and its update frequency. Today you can also analyze site traffic, competitors, or the most popular keywords used by competitor's customers.
SimilarWeb. This service shows useful data blocks: geography, traffic channels, detailed information about the user path, audience interests, general, social, and search traffic. You just need to indicate the domain of the competitor's website in the upper left corner of the main page without registration.
Sucuri. This app checks website for malware, blacklists, bugs, and outdated software.
Quttera Web Threat Scanner. This software is a cloud-based application that scans websites and generates security reports. An online antivirus scanner analyzes website URLs and checks for suspicious scripts, malicious files, and other online threats.
URLVOID. This service analyzes a website through several blacklisting mechanisms and online reputation tools to make it easier to detect fraudulent and malicious resources. It helps you identify websites associated with malware, scams, and phishing websites.
IoT search engines
Internet of Things (IoT) search engines are like Google Search but for devices connected to the Internet. You can use Nmap to scan ports, services, and protocols actively, but with Shodan.io, you will have access to information about the ports already available. This service is used not only by security researchers worldwide but also by marketers who collect data about buyers. Alternatively, you can use Censys or its Chinese equivalents, Fofa and ZoomEye.
Location search
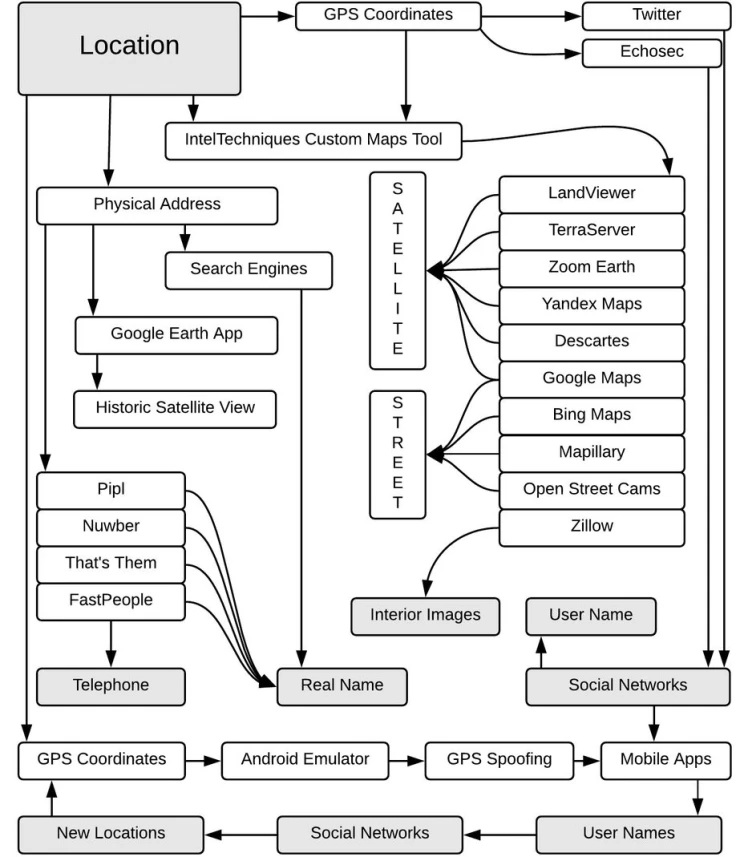
Geolocation tools

Creepy is a free tool for locating people using social media and image-sharing sites. Its paid analog is Echosec , which costs about $500 per month.
IP-based geolocation
Many sites help match an IP address with a location as IPlocation.net does. But if you know the Wi-fi points to which the target was connected, you can use Wigle.net. This service will help you map and conduct a more detailed study.
Some other useful websites are:
Emporis operates a worldwide database of construction data and commercial real estate information.
EarthCam is a world leader in webcam content, technology, and services.
Inescam is the world's largest catalog of CCTV cameras online.
Images
Google Images , Bing Images and Baidu Images allow you to perform a reverse image search to see where else they were used or when they were first published. We also recommend using the Tineye service as it has slightly different algorithms than Google, which means the results may differ. Researchers can identify people by their avatars because people rarely update their social media profile photos. It can also be useful to debunk fake news. A journalist can perform an image search in combination with filtering.
You can use special tools to find images depending on purpose and format. For example, Findclone and Findmevk.com can be used for Vkontakte, while Karmadecay is better for Reddit. You can also install browser extensions such as RevEye for Chrome and Image Search Options for Firefox. Or download mobile app CamFind for IoS.
The image itself contains much EXIF data, such as camera information, geo-coordinates, and other details. If it's not removed, some interesting things can be found. For example, if you know the geo-coordinates, you can determine where the picture was taken. For this purpose, you can use image editing tools or online resources such as Exifdata or View EXIF Data. To remove EXIF data from your image, you can use EXIF Purge or VIEW AND REMOVE EXIF ONLINE
If you need to find out if the image has been somehow altered or faked, you can use the application to conduct a forensic examination. If you don't want to upload the image online, analyze it locally with Phoenix or Ghiro.
Automating OSINT
Searching for information manually can be time-consuming, and automatic tools can pick up correlations that you might miss. The decision to use these tools will depend on your specific situation, as most of them require training but are essential for complex tasks. So, if you need to perform a few simple tasks, it is better to use the online services that we have described above.
Below are the tools to help you automate the process.
SpiderFoot
SpiderFoot is a utility designed to automate the collection of intelligence information (represented by an IP address or domain name). Unlike its Maltego analog, SpiderFoot's interface is available in the browser. Various methods can be used to collect information about the target, such as web scanning, blacklisting queries, or collecting information using all open sources.
theHarvester
theHarvester can collect email addresses, domain names, and sites related to the same IP as the searched servers. For passive intelligence, theHarvester uses Bing, Baidu, Yahoo, Google, and social networks. For active reconnaissance, it performs DNS reverse search, DNS TDL expansion, and DNS enumeration.
Maltego
Maltego is a comprehensive graphical link analysis tool that offers real-time data mining, information collection, and a node-based graph representation. It helps identify patterns and relationships between different parts of information.
FOCA
FOCA is a tool for obtaining confidential information and metadata. It performs metadata analysis to understand which documents were created by the same person. One of its main disadvantages is that the latest version is only available for Windows.
Conclusion
In the era of post-confidentiality, it is extremely difficult to control information floating in this digital ocean, and even more so to maintain privacy. If you cannot control it, it is important to at least understand what is happening. After all, one who masters information, masters the world.
***
📌 For everyone who really wants to learn OSINT, we recommend OSINT training courses from Molfar:
▪️ Basic: for personal study and receiving a knowledge base + all the necessary tools for work.
▪️ Advanced: for scaling processes, gathering a team and learning HUMINT.