OSINT (open-source intelligence) is a process of data collection from all possible resources that have open access. There are thousands of such resources, and accordingly, there are dozens of techniques intended for their study.
If we consider "technique" as any possible way and mechanism used by many OSINT tools, then we can find hundreds of them. For example, we can search by keywords, hashtags, parts of code, username, phone number, etc. However, if we look at the fundamental differences in approaches, they can be grouped into three main techniques. We will consider them below with examples.
OSINT Techniques for Comprehensive Open Source Intelligence
Exploring Publicly Available Data
One of the primary OSINT techniques revolves around collecting and analyzing public data. This approach is often utilized by both organizations and individuals, serving various purposes. Its core objective is to uncover publicly accessible information that may have security implications or the potential to expose sensitive details.
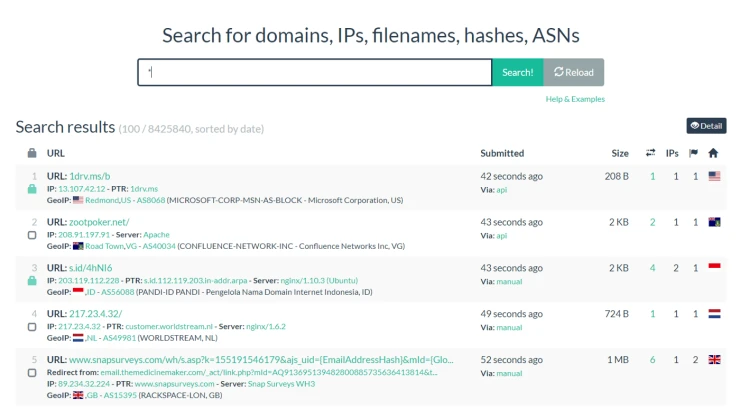
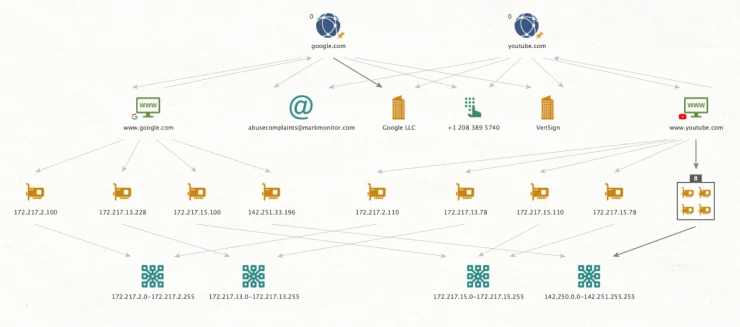
For instance, WHOIS offer valuable data, including addresses, names, and phone numbers linked to domain registrations. Complementing this, services such as URLscan.io or DomainIQ provide insights into IP addresses, enhancing our understanding of specific website ownership.
Even without such specialized information, open-source searches can help hackers steal someone's profile. For example, if a stalker wants to access a person's page, they only need to know answers to code questions to recover the password. For instance, they can find your mom's maiden name and pet's name in old social media posts.
For this reason, this technique is used to find potentially security-threatening information and remove it.
Searching for information outside the company to find security breaches
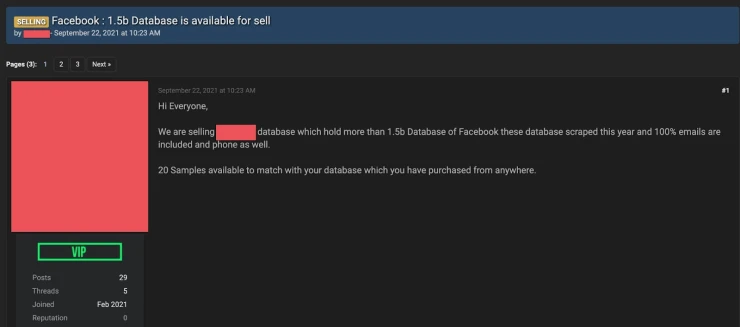
While similar to the previous technique, this approach takes a different angle. Here, OSINT specialists actively seek information that has become publicly available due to security breaches. Such data may emerge on the visible layers of the internet. For instance, leaked photos originally shared privately through messages can surface publicly, indicating a security lapse.
This technique involves monitoring data exposure due to account compromises or unauthorized sharing of information. Proficiency in scanning the deep and dark web is often essential, using tools like Tor (The Onion Router) to uncover leaked company databases, highlighting vulnerabilities in their security systems.
Threat Hunting and Utilizing Threat Intelligence Tools
This technique is a logical continuation of the previous one. Specialists must track how information leaked into the public domain and why it happened. For example, in one case, the problem may be in the software, which left a loophole for hackers. In another case, the reason may be much simpler: an employee accidentally or deliberately leaked sensitive information.
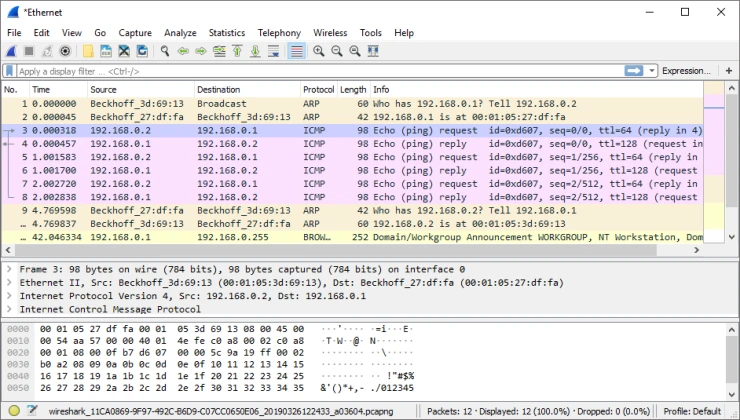
Moreover, this technique can be used to identify the problem separately. Usually, investigators use tools that require specialized technical knowledge to use threat intelligence platform or tools. For example, Wireshark analyzes and supports the decryption of hundreds of protocols, and Nmap software checks ports. For many of us, this information means nothing. However, IT professionals can see security weaknesses and fix them.
Analysis and comparison of data
Regardless of the specific OSINT technique employed, the analysis and correlation of data are fundamental to the investigative process. Information collected from various sources must be meticulously examined, categorized, and cross-referenced to draw meaningful conclusions. This analytical process extends to discerning mobile phone ownership details, establishing connections across diverse social media profiles, or unraveling intricate relationships between individuals and organizations. Advanced tools like Maltego provide the capability to organize data into structured visualizations, facilitating the identification of complex linkages within extensive datasets.
In summary, these OSINT techniques serve as indispensable instruments for conducting open-source intelligence investigations. While some objectives may be accomplished using a single technique, others demand the strategic integration of multiple methodologies. Ultimately, the key lies in the adept analysis and correlation of data, whether through dedicated tools or methodical reasoning.
Are OSINT Techniques Legal?
The realm of Open Source Intelligence (OSINT) straddles a fine line between what's legal and what isn't, largely depending on the jurisdiction and methodologies in play. Generally speaking, OSINT involves gathering information from sources that are publicly accessible. In many countries, accessing this public information is legal. However, challenges arise when considering how this information is obtained, the intent behind its acquisition, and its subsequent use.
For instance, in the United States, OSINT practices are mostly viewed through a legal lens due to their reliance on public data. But there are caveats. Activities that involve unauthorized access to computer systems, even if they seem to be publicly available, could breach laws like the Computer Fraud and Abuse Act (CFAA). Similarly, in the European Union, the introduction of the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) hasn't made OSINT illegal, but it has necessitated caution, especially when personal data is involved.
Venturing into countries like Russia or China introduces additional complexities. Russia's stringent internet laws mean that even though OSINT isn't prohibited, the broad interpretation of its regulations can make some data collection methods risky. Meanwhile, in China, the state's tight control over online data implies that accessing certain public information might not be illegal in itself, but disseminating it, especially if perceived as detrimental to national interests, could be.
Beyond the legal landscape, ethical considerations are also pivotal. Just because information exists in the public domain doesn't mean its acquisition or dissemination is ethically justified. It's essential to respect privacy nuances, even with seemingly public data. Some countries have even instituted protective measures against OSINT misuse, requiring declarations of intent before data access.
The purpose behind data collection can also influence its legality. While gathering data for personal enrichment might not raise eyebrows, using it for commercial gains, defamation, or manipulation can lead to legal repercussions.
In conclusion, while OSINT operates largely within the public domain, it doesn't grant unrestricted rights to gather or use information. Those involved in OSINT must be aware of and adhere to the legal and ethical boundaries their activities might encounter.
Conclusion
All these techniques can be used for OSINT investigation and are self-contained. For some purposes, one of these techniques can be sufficient, but other cases require consistent use of all of them. The main thing is to analyze and compare data by using tools or just rational thinking.
Open Source Intelligence (OSINT) refers to the process of collecting, analyzing, and making decisions based on publicly available information. The advantages of OSINT include:
- Cost-Effective: OSINT utilizes publicly available sources, which eliminates the need for expensive data acquisition methods or tools.
- Timely Information: OSINT tools and techniques can gather real-time data from various online platforms, ensuring up-to-date intelligence.
- Broad Coverage: OSINT covers a vast array of sources, from news websites and social media platforms to public records and academic publications, offering comprehensive insights.
- Flexibility: OSINT can be applied across various domains, from cybersecurity and law enforcement to market research and journalism.
- Reduced Risks: By relying on open sources, OSINT reduces the legal and ethical risks associated with intrusive intelligence-gathering methods.
In the digital age, where information is abundant and readily accessible, OSINT provides a valuable method for organizations and individuals to stay informed and make data-driven decisions.
***
📌 For everyone who really wants to learn OSINT, we recommend OSINT training courses from Molfar:
▪️ Basic: for personal study and receiving a knowledge base + all the necessary tools for work.
▪️ Advanced: for scaling processes, gathering a team and learning HUMINT.